Auditable unit testing
In this tutorial, you will learn how setup a unit test and make it ready for auditability purposes.
Arrange
-
Have a basic ADM-setup on your Git-repo using for example this guide: How-to: setup Gitlab repository
-
A valid ADM license added to the /environment directory
Act
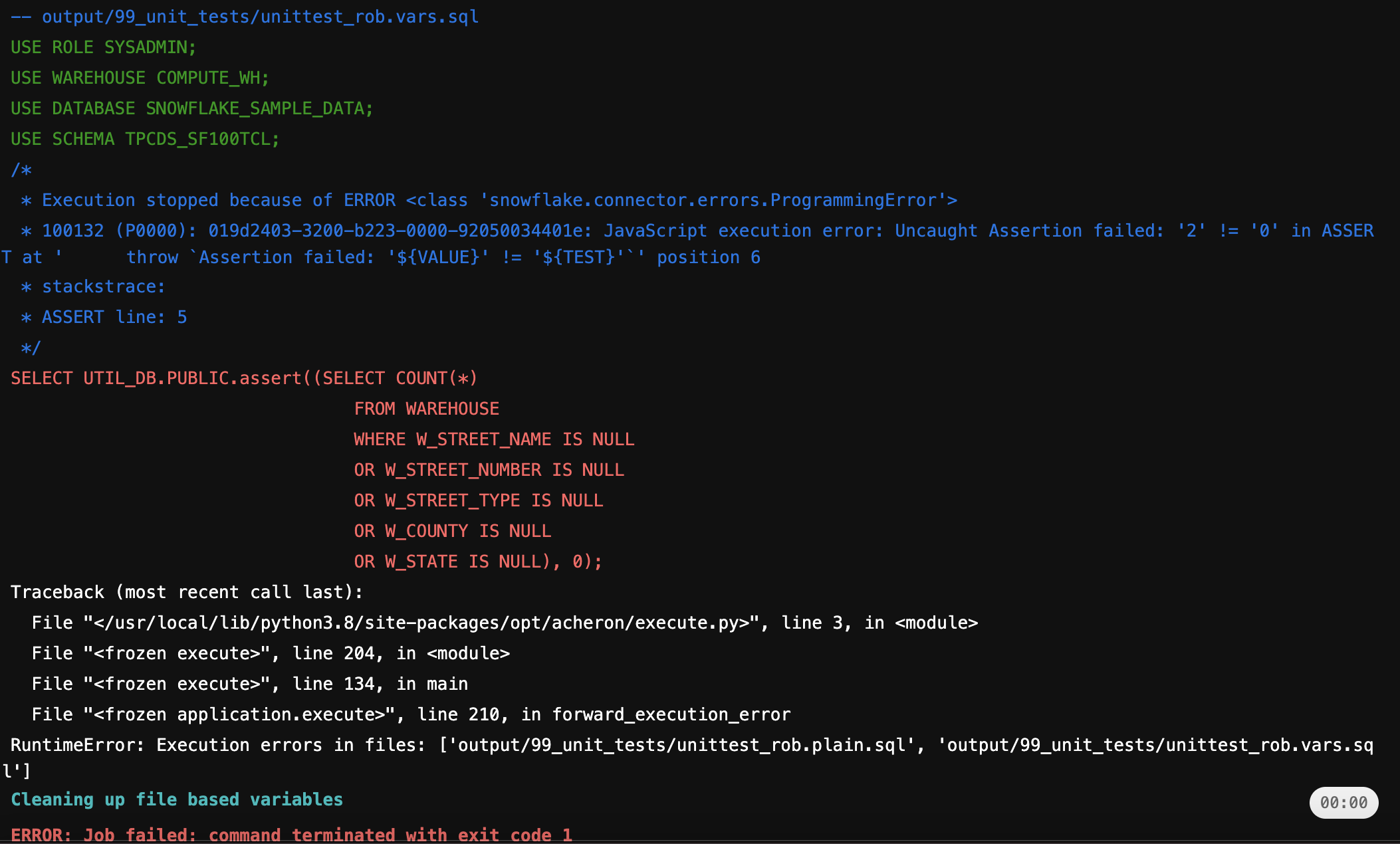
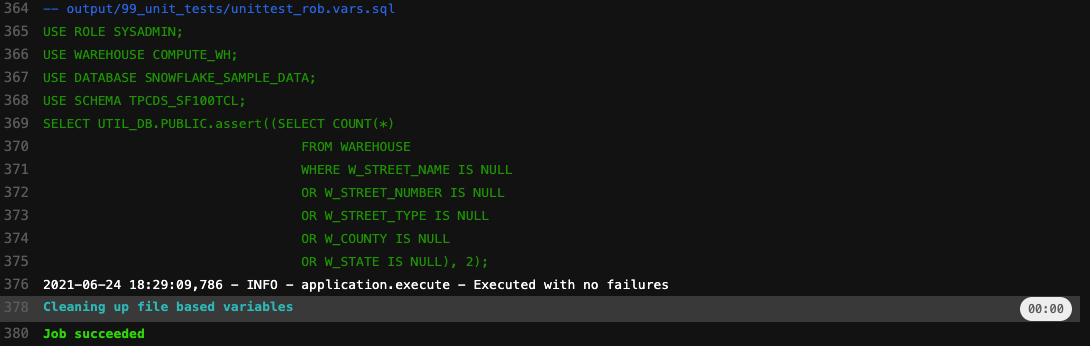
For unittesting purpose we use the assert statement. It helps detect problems early in your data landscape, where the cause is clear, rather than later when some other operation fails. Assert terminates the transaction (usually with a message quoting the assert statement) if its argument turns out to be false.
Within this example we use a table where store warehouse information are stored with their address and let’s say that we want to check if we have store warehouse with a incomplete address.
USE ROLE RL_ADMIN;
USE WAREHOUSE COMPUTE_WH;
USE DATABASE SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA;
USE SCHEMA TPCDS_SF100TCL;
SET var_expected = 0;
SET var_actual = (SELECT COUNT(*) (1)
FROM WAREHOUSE
WHERE W_STREET_NAME IS NULL
OR W_STREET_NUMBER IS NULL
OR W_STREET_TYPE IS NULL
OR W_COUNTY IS NULL
OR W_STATE IS NULL);
SELECT UTIL_DB.PUBLIC.assert($var_actual, $var_expected); (2)| 1 | A variable is set with the outcome of a count statement on de warehouse address information |
| 2 | Assert function |
Commit and Push the new unit-test to /output/99_unit_test