How-to: setup Database accounts
In this how-to, we describe how you can setup a Database account. At the end of this how-to-guide, you will have a account which you use for provision your cloud database.
Supported databases
How-to: setup Snowflake account
In this how-to, we setup an existing snowflake account. At the end of this how-to-guide, you will have a snowflake account which you use for provision your Snowflake cloud database.
-
Have an Snowflake account that you own. Or simply create one.
-
Create a Snowflake user. Example: Listing 1. Create Snowflake user
-
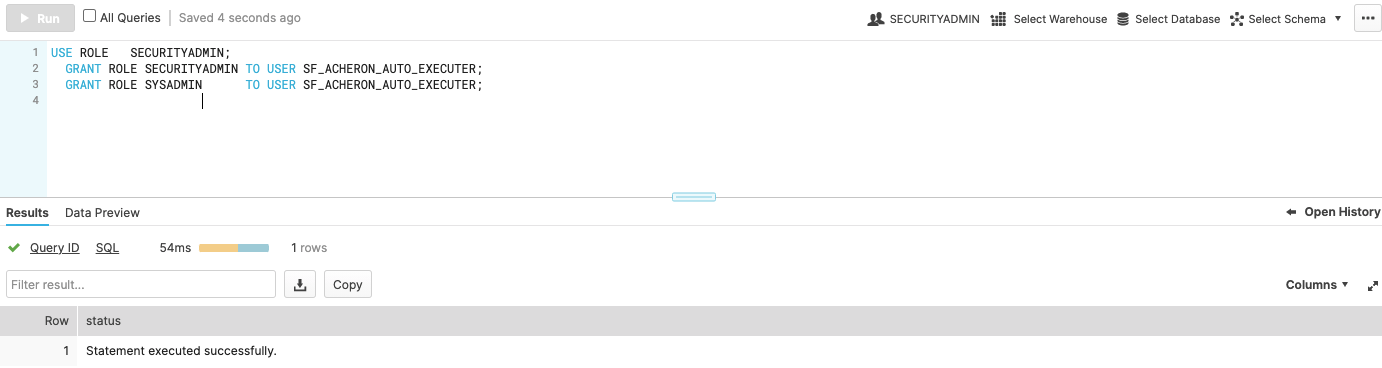
Assign the proper execution rights to the user. Example: Listing 2. Assign roles SYSADMIN and SECURITYADMIN
USE ROLE IDENTIFIER('SECURITYADMIN');
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS IDENTIFIER('SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER')
PASSWORD = '<developments-snowflake-password>' (1)
MUST_CHANGE_PASSWORD = FALSE
DEFAULT_ROLE = 'PUBLIC'
DEFAULT_WAREHOUSE = NULL;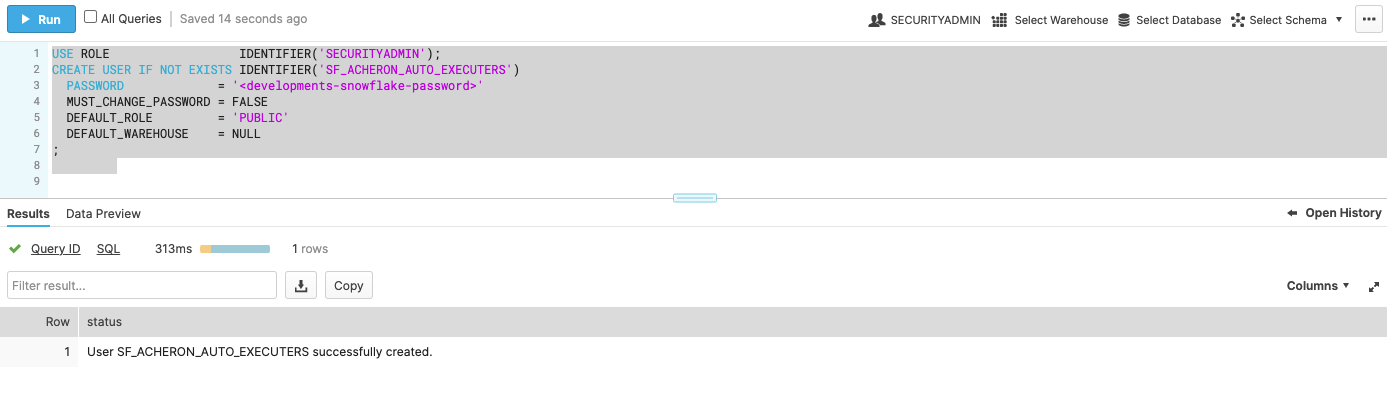
USE ROLE SECURITYADMIN;
GRANT ROLE SECURITYADMIN TO USER SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER;
GRANT ROLE SYSADMIN TO USER SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER;| 1 | We recommend RSA-private-keys for production-like environments instead of user/password-combinations. |
How-to: setup Google BigQuery account
In this how-to, we setup an existing Google BigQuery account. At the end of this how-to-guide, you will have a Google BigQuery account which you use for provision your Google BigQuery cloud database.
-
Have an Google BigQuery account that you own. Or simply create one.
-
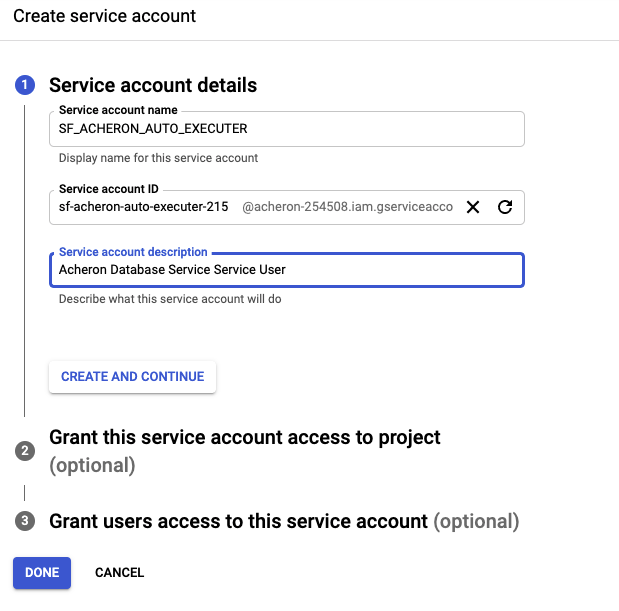
Create a Google BigQuery Service account, follow the google guide.
A service account is a Google Account that is associated with your Google Cloud project. Use a service account to access the BigQuery API if your application can run jobs associated with service credentials rather than an end-user’s credentials, such as a batch processing pipeline.
-
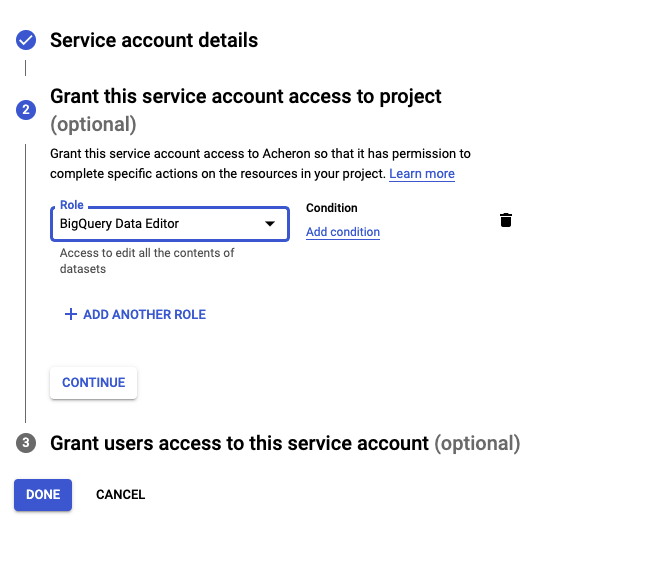
Select your project and create service account for Acheron service user
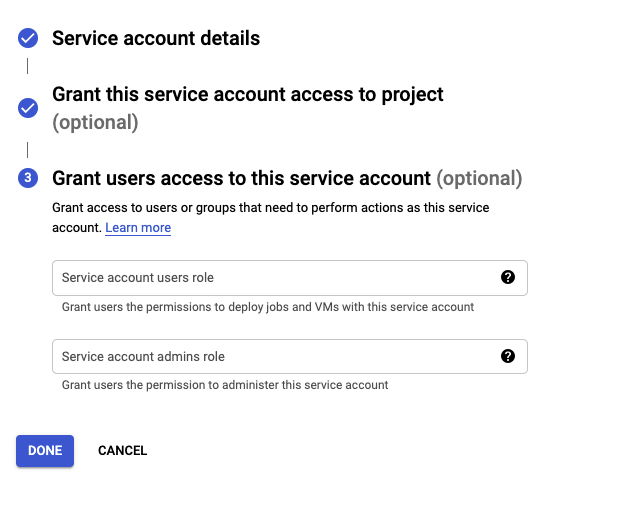
-
Select your created service account and go to tab "KEYS", click add keys
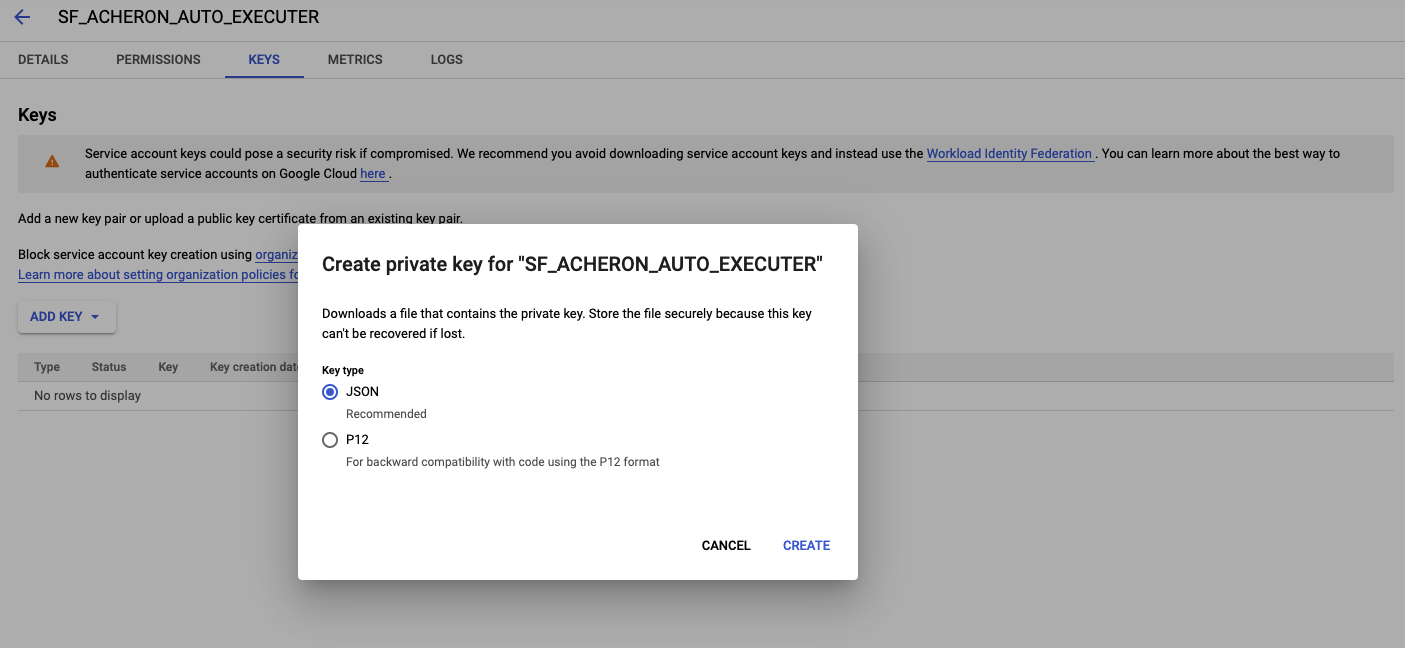
-
Save the downloaded key file in your secret vault. In the Git Repository you can store the content as a secret environmental variable for use, for example How-to: setup Gitlab
How-to: setup Azure SQL account
At the end of this how-to-guide, you will have a Azure account where its Azure SQL cloud database is connected to ADM.
-
Database tool, for example Azure Database Studio
-
An active Azure subscription. If you don’t have one, create a free account here
-
Create an Azure SQL Database using this tutorial.
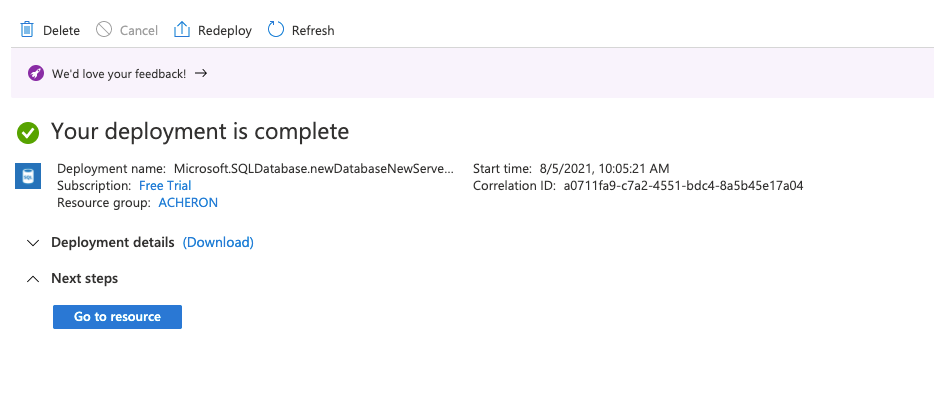
Note that after this setup, the azure-account with which the DB is created is automatically the server administrator. Hence, this account has access to the Azure SQL Database as well.
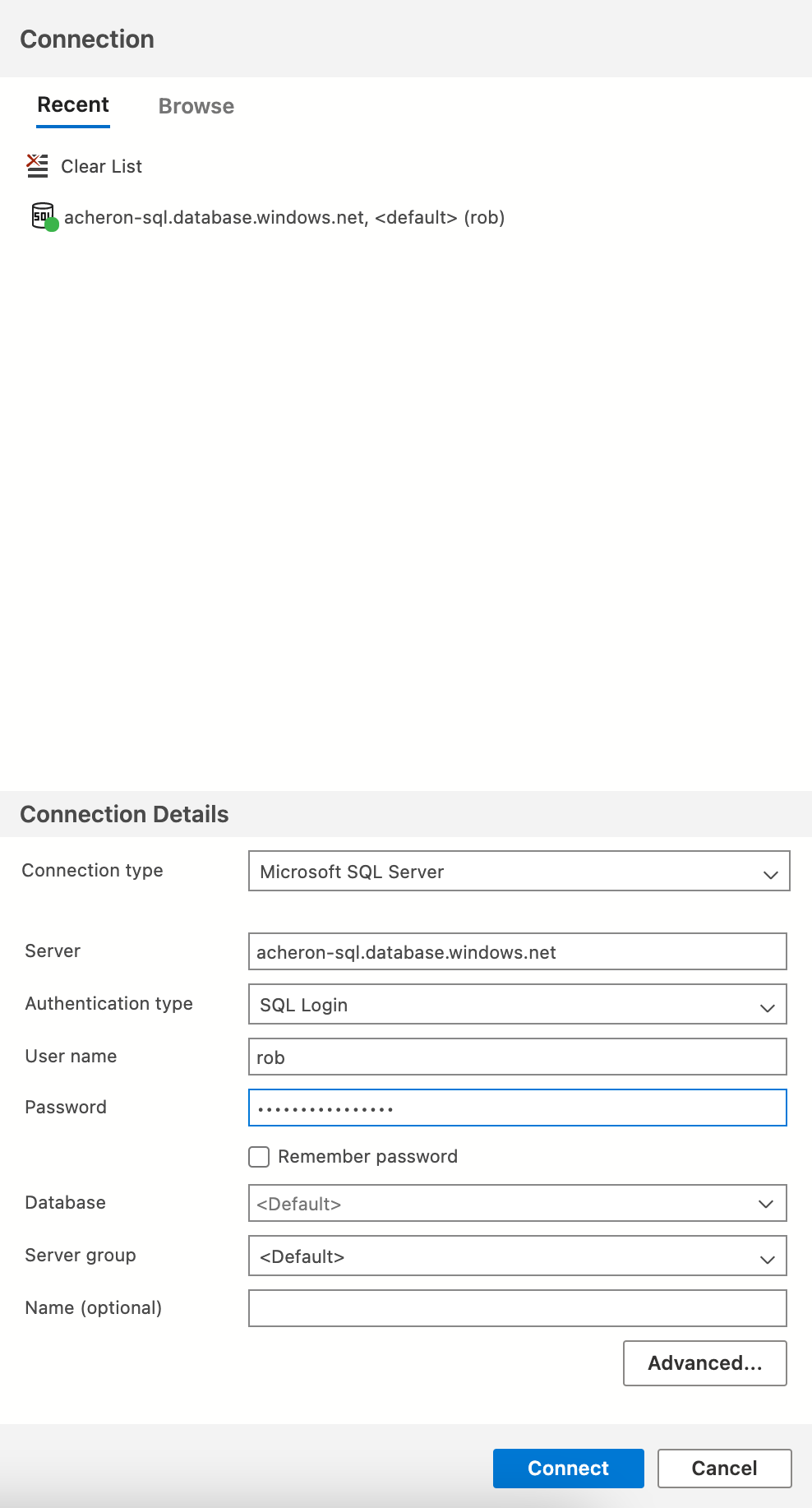
-
Let’s create a login for the Acheron service user on the master database
CREATE LOGIN SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER WITH password='<acheron-azure-password>';-
Make a connection to your database and create a user for the acheron service user
CREATE USER SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER FROM LOGIN SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER;
-
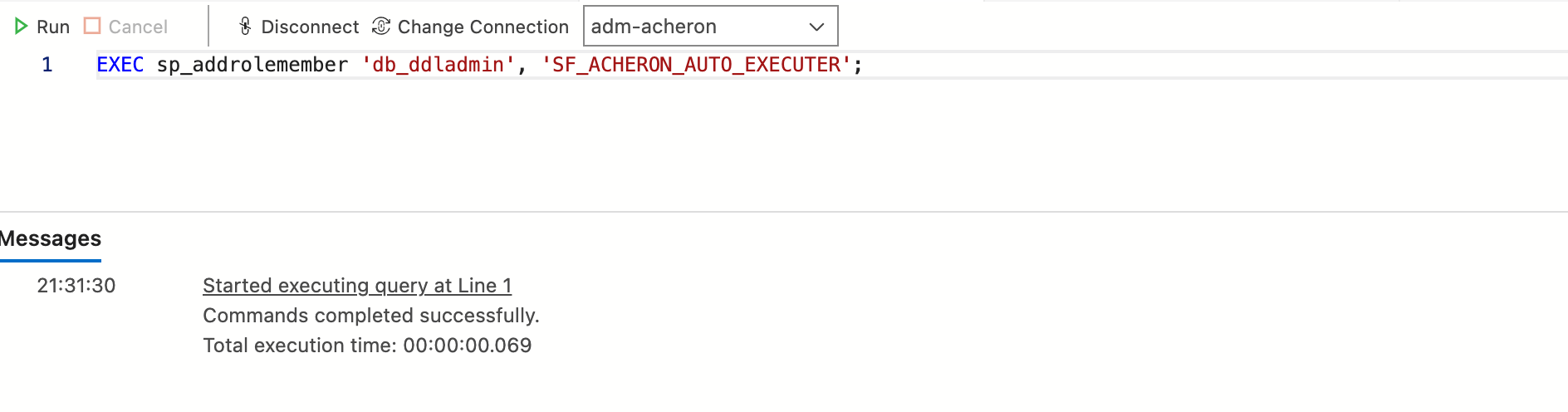
Give the new user rights on the database
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_ddladmin', 'SF_ACHERON_AUTO_EXECUTER';
-
Save the user en password in your secret vault. Next, assign the username and password as environment variables in Gitlab/Github. Check-out these tutorials for the steps in detail: Github-setup Gitlab-setup